Journal #Three [DAT701] - ETL Process
![Journal #Three [DAT701] - ETL Process](/assets/images/dat701-j3.jpg)
ETL Process
JOURNAL #THREE [DAT701]
ETL Process
Business Process
A business process in dimensional modelling is identified and described through the classification of a set of related business activities that have the highest importance to stakeholders. Business processes will not necessarily relate to business departments, and instead might revolve around customers, sales, profit, and products. For example, an organisation might have a sales department and marketing department, both will be interested in order data as the recognised business process. Dimensional models should be constructed around the business process to limit duplication or data redundancy, which can lead to problems and inconsistencies with data quality. In the case of FinanceDB, two business processes have been identified:
- Sales Performance
- Sales Orders
After the business processes have been identified they must be prioritised. To clarify the priority level several criteria must be considered:
- Strategic significance and scope of the business process
- Availability and quality of data in the source system
- Feasibility of the process and its complexity
- Other factors specified as important to the business process
Defining business processes allows for the high-level entities that are common across the processes to be identified and grouped to create shared dimensions. In the case of FinanceDB, these have been determined as:
- Date
- Sales Representative
- Region
- Product
It is important to identify these common entities early in the development lifecycle, to allow business stakeholders to agree on the definitions to ensure consistency across the organisation. This is crucial to mitigate the risk of entities changing once the data warehouse is in production, which can impact the ETL process and applications that rely on the definitions, such as the business intelligence tools.
Granularity
The level of granularity that will be required in the fact tables can be determined from the business processes, and the requirements gathering conducted as part of the systems development. Documents collected in the requirements gathering process will often contain information that can be used to define the grain of measurement stores in the fact tables. The level of the grain should convey the exact contents of a measurement record stored in the fact table. The greater the level of detail included, the lower the level of granularity, conversely, if there is less detail included in the record, the granularity level will be higher.
The level of detail available in a dimensional schema is the grain, and each fact and dimension table in the schema will have separate granularity. The dimensional schema’s grain is defined as the finest level of detail that can be realised by joining the fact and dimension tables. The grain defined in the FinanceDW model consists of dimensions Date, Sales Representative, Product, and Region, meaning the granularity obtained extends to the date a product was sold by region and sales representative.
The grain of the fact tables is based on the business questions listed in Assignment 1. In a business scenario, additional information may be produced such as invoices, order forms, and any access granted to business operation applications. These documents and applications can also point to entities such as customer or product that can form the dimension tables. High-level or preliminary measures that are easy to identify should be considered first to define the grain, these measures can include unit price, manufacturing price, and cost. These measures may not be the final set of measurements included in the fact tables, however, they can support formal measures for the fact tables.
The FinanceDW data warehouse contains two business processes that form the two fact tables. Several preliminary measurements have been incorporated in the FactSaleOrder table to support future proofing and to be able to quickly answer business questions that may not have been identified in the requirements gathering process. The measurements in the fact tables extend to the dimension tables, which includes data that allows performance data to be aggregated annually and monthly, and further related to both the sales representative and region tables. The sales order table aggregates measurements to total sales relating to an order, with granularity to the product level. The fact table measurements constitute multiple granularities within the single fact, the columns have been named to specifically identify the granularity level of the records represented by the column, such as TotalAnnualKPI and TotalMonthlyKPI.
- Sale Performance (Fact)
By Date (Granularity to the Month) (Dim)
By Region (Granularity to the Country and Segment) (Dim)
By Sales Representative (Granularity to the Sales Representative Name) (Dim)
- Sale Order (Granularity to the Sales Order ID) (Fact)
By Date (Granularity to the Day) (Dim)
By Region (Granularity to the Country and Segment) (Dim)
By Sales Representative (Granularity to the Sales Representative Name) (Dim)
By Product (Granularity to the Product Name) (Dim)
User Access & Security
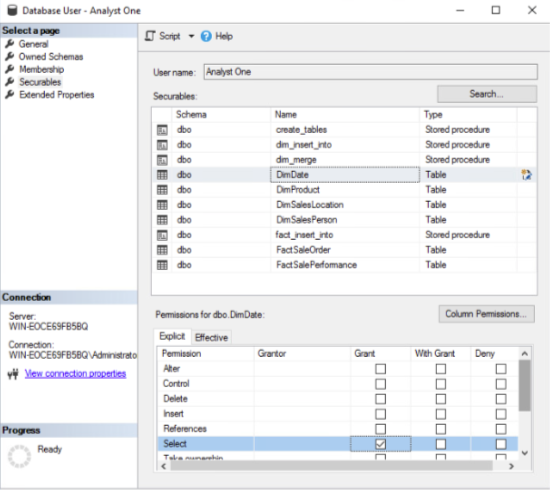
To ensure the operational integrity of the OLTP FinanceDB database, access permissions have been granted to the Data Warehouse Developer. The developer does not require permissions that extend beyond READ, therefore select has been granted to this user. The permissions granted are a set of governing rules that determine the access level given to a user. Further permissions can be applied such as grant, revoke, and deny. Two further users have been created in the FinanceDW data warehouse for the data analysts to READ the data from the business intelligence tool.
Users have been set up using two available processes in SQL Server:
- T-SQL statement
- SQL Server Management Studio Wizard
These methods have been used to create the necessary login, the users, and the permissions associated with those users. The processes have been recorded in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, and Figure 11.
-- >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-- Create User Login and assign permissions for Data Warehouse Developer to read only access FinanceDB
use FinanceDB;
create login data_Warehouse_Developer with password = 'P@ssword1';
create user data_Warehouse_Developer for login data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.Country to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.Product to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.ProductCost to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.Promotion to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.Region to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.SalesKPI to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.SalesPerson to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion to data_Warehouse_Developer;
grant select on FinanceDB.dbo.Segment to data_Warehouse_Developer;
-- Create User Login and assign permissions for Data Analyst Manager to read only access FinanceDW from PowerBI
use production_FinanceDW;
create login data_Analyst_Manager with password = 'P@ssword1';
create user data_Analyst_Manager for login data_Analyst_Manager;
grant select on DimDate to data_Analyst_Manager;
grant select on DimProduct to data_Analyst_Manager;
grant select on DimSalesLocation to data_Analyst_Manager;
grant select on DimSalesPerson to data_Analyst_Manager;
grant select on FactSaleOrder to data_Analyst_Manager;
grant select on FactSalePerformance to data_Analyst_Manager;
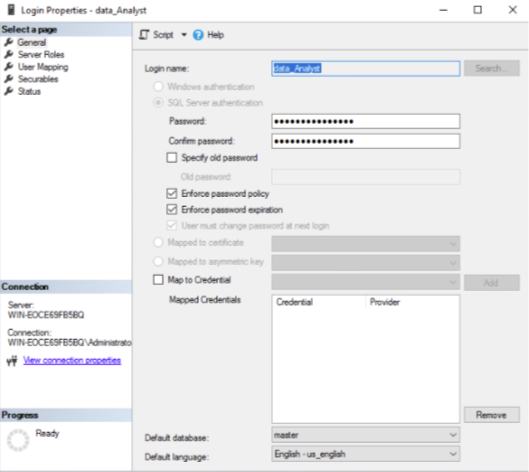
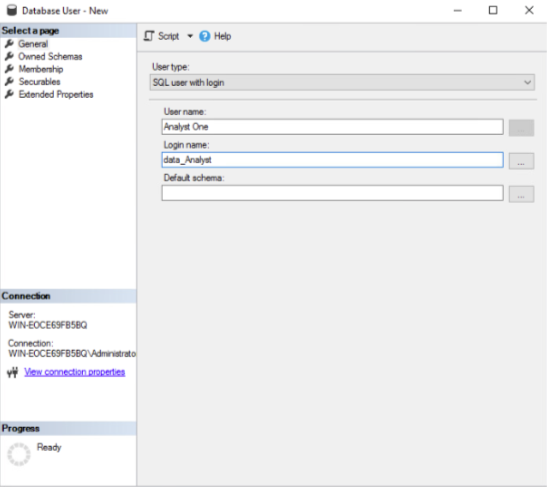
The following figures show the same process represented in Figure 8, a further data analyst having been created in the data warehouse using the built-in Login Properties and Database User wizards.
Dimensions and Facts
ETL of the operational data has been performed through the use of two procedures and two views. The first procedure performs a complete bulk update of all the data ingested into the data warehouse as an initial ingestion of data and has been included in Appendix A. A further method has been created and has been included in Appendix B. This method deploys a variation of UPSERT in SQL Server called MERGE, which aims to update column records in the data warehouse for tuples that already exist in the fact or dimension tables, insert data where new information has been added to the OLTP database, or delete data that has been removed. UPSERT is an acronym for update and insert in T-SQL.
Merge is an operation that runs insert, update, or delete on a target table defined in the statement, in this case, FinanceDW, and joins it with the source database, FinanceDB. The merge statement effectively synchronises the two tables based on the differences that have been identified. This is accomplished through the use of the following terms:
when matched then– when this is satisfied by the search condition the tuples are either updated or deleted. Merge statements can have twowhen matchedclauses, with the second clause applied only if the first has not been applied.when not match then– specifies that the row will be inserted into the target table. Merge statements can only contain onewhen not matchclause.
Common table expressions have been deployed for the dimension tables, acting as the temporary name for the result set, the merge statement references the common table expression naming structure. The fact tables are more complex due to the granularity of the measures and the relationships to the dimension tables, these require multiple common table expressions that are not capable of being referenced by the merge function. This required the fact table queries to be wrapped inside a view, these views can then be referenced by the merge statements to perform the UPSERT event.
To test the merge statements, data was changed in the FinanceDB database after the bulk insert procedure was run and the data set was successfully stored in the FinanceDW data warehouse. The merge statements showed that the changed data was updated as expected in the data warehouse.
Data ETL for Dimensional Tables and Fact Tables
The two ETL procedures created for the FinanceDW data warehouse are wrapped in stored procedures. The completed procedures including the views created for the merge statements can be found in Appendix A and Appendix B.
An alternative DimDate table has been considered and created that uses the dates contained across the tables in the FinanceDB database. The table takes the sales order date as the date key and includes the sales KPI year and promotion year as dates through the union select statement using the convert function. The day, month, and year have been extrapolated as integers from the collection of distinct dates. Figure 12 shows the process used to create this table.
-- >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-- Alternative DimDate based on dates in FinanceDB
drop table if exists DimDate_AltVersion;
go
create table DimDate_AltVersion
(
[Date_Key] datetime primary key,
[Day] int not null,
[Month] int not null,
[Year] int not null
);
go
drop view if exists DateView_AltVersion;
go
create view DateView_AltVersion as
with dd_av(NewDate) as
(
select SalesOrderDate from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder
union
select convert(datetime, convert(varchar(10), SalesYear)) from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesKPI
union
select convert(datetime, convert(varchar(10), PromotionYear)) from FinanceDB.dbo.Promotion
)
select distinct
NewDate as [Date_Key],
day(NewDate) as [Day],
month(NewDate) as [Month],
year(NewDate) as [Year]
from dd_av
where
NewDate is not null;
go
select * from DateView_AltVersion
order by [Date_Key] desc;
go
merge into DimDate_AltVersion as Target
using DateView_AltVersion as Source
on Target.[Date_Key] = Source.[Date_Key]
when matched then
update set
Target.[Date_Key] = Source.[Date_Key],
Target.[Day] = Source.[Day],
Target.[Month] = Source.[Month],
Target.[Year] = Source.[Year]
when not matched then
insert ([Date_Key], [Day], [Month], [Year])
values (Source.[Date_Key], Source.[Day], Source.[Month], Source.[Year]);
go
select * from DateView_AltVersion;
go
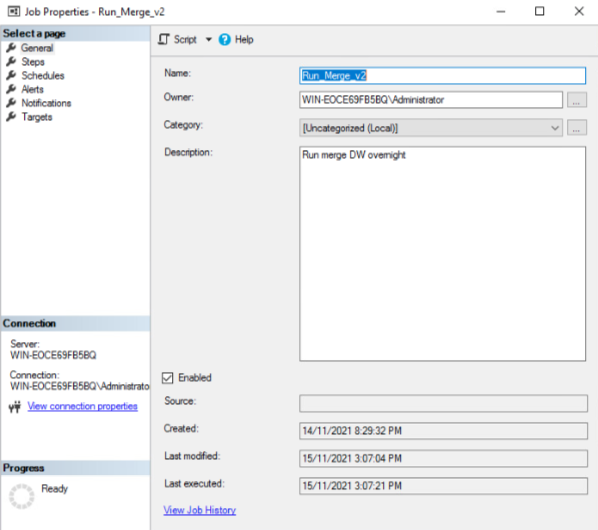
Research was conducted to find a solution that would allow the ETL merge procedure to be performed on a schedule when access is likely to be limited resulting in a low demand on system resources, such as overnight. SQL Server Agent was used to create a job that would run the procedure automatically, the process to establish the run merge procedure can be viewed in Figures 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17.
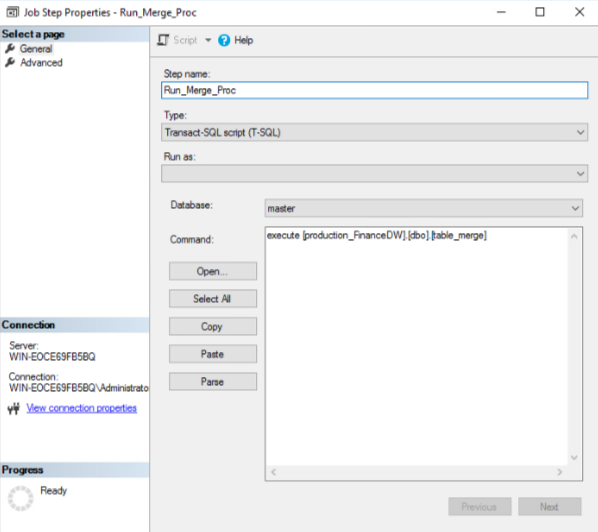
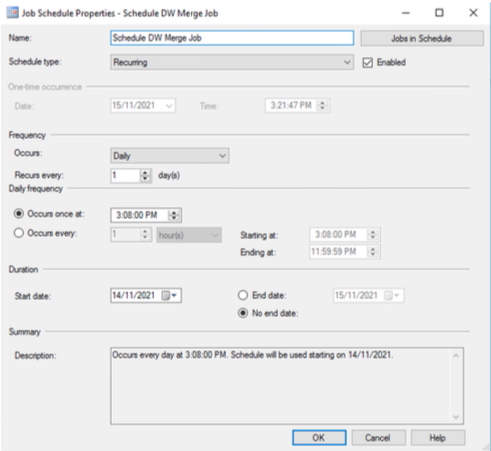
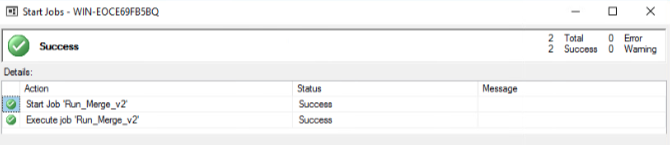

Convert datetime to integer. (n.d.). Retrieved October 17, 2021, from https://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/04f2098e-9802-4fea-a936-3f988981f8ee/convert-datetime-to-integer?forum=transactsql
Converting dates to integer. (n.d.). Kimballgroup.Forumotion.Net. Retrieved October 17, 2021, from https://kimballgroup.forumotion.net/t720-converting-dates-to-integer
Data Transformation and Data Quality. (n.d.). Stitch. Retrieved November 10, 2021, from https://www.stitchdata.com/platform/datatransformation/
data warehouse—Loading Fact Tables with SQL Server. (n.d.). Stack Overflow. Retrieved October 17, 2021, from https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10053002/loading-fact-tables-with-sql-server
Execute Stored Proc Using SQL Job. (n.d.). Retrieved November 14, 2021, from https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/execute-stored-proc-using-sql-job/
How to Run a SQL Server UPSERT using Merge. (2020, August 14). HackDeploy. https://hackdeploy.com/how-to-run-a-sql-server-upsert-using-merge/
MS SQL Server—How to get Date only from the datetime value? (2018, September 1). TablePlus. https://tableplus.com/blog/2018/09/ms-sql-server-how-to-get-date-only-from-datetime-value.html
Peterson, R. (2020, March 16). How to Create Login, User & Assign Permissions in SQL Server. https://www.guru99.com/sql-server-create-user.html
Populating Fact Tables. (2015, February 9). Data Warehousing and Machine Learning. https://dwbi1.wordpress.com/2015/02/09/populating-fact-tables/
Sql server—How to automatically run a stored procedure on scheduler basis? - Stack Overflow. (n.d.). Retrieved November 14, 2021, from https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12158158/how-to-automatically-run-a-stored-procedure-on-scheduler-basis
tsql - How do I get the month and day with leading 0’s in SQL? (E.g. 9 => 09). (n.d.). Stack Overflow. Retrieved November 4, 2021, from https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13804096/how-do-i-get-the-month-and-day-with-leading-0s-in-sql-e-g-9-09
UPSERT Functionality in SQL Server 2008—DatabaseJournal.com. (n.d.). Retrieved November 6, 2021, from https://www.databasejournal.com/features/mssql/article.php/3739131/UPSERT-Functionality-in-SQL-Server-2008.htm
XiaoyuMSFT. (n.d.). MERGE (Transact-SQL)—SQL Server. Retrieved November 6, 2021, from https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/merge-transact-sql
Appendices
Appendix A
-- >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-- Inserting into tables
-- https://docs.oracle.com/database/121/DWHSG/transform.htm#DWHSG8313
drop procedure if exists insert_into;
go
create procedure insert_into
as
begin
-- DimDate
-- https://gist.github.com/sfrechette/0be7716d98d8aa107e64
declare @DateCalendarStart datetime,
@DateCalendarEnd datetime,
@FiscalCounter datetime,
@FiscalMonthOffset int;
set @DateCalendarStart = '2000-01-01';
set @DateCalendarEnd = '2030-12-31';
-- Set this to the number of months to add or extract to the current date to get the beginning
-- of the Fiscal Year. Example: If the Fiscal Year begins July 1, assign the value of 6
-- to the @FiscalMonthOffset variable. Negative values are also allowed, thus if your
-- 2012 Fiscal Year begins in July of 2011, assign a value of -6.
set @FiscalMonthOffset = 0;
with DateDimension
as
(
select @DateCalendarStart as DateCalendarValue,
dateadd(m, @FiscalMonthOffset, @DateCalendarStart) as FiscalCounter
union all
select DateCalendarValue + 1,
dateadd(m, @FiscalMonthOffset, (DateCalendarValue + 1)) as FiscalCounter
from DateDimension
where DateCalendarValue + 1 < = @DateCalendarEnd
)
insert into dbo.DimDate (DateKey, FullDate, DayNumberOfWeek, DayNameOfWeek, WeekDayType,
DayNumberOfMonth, DayNumberOfYear, WeekNumberOfYear, MonthNameOfYear,
MonthNumberOfYear, QuarterNumberCalendar, QuarterNameCalendar, SemesterNumberCalendar,
SemesterNameCalendar, YearCalendar, MonthNumberFiscal, QuarterNumberFiscal,
QuarterNameFiscal, SemesterNumberFiscal, SemesterNameFiscal, YearFiscal)
select cast(convert(varchar(25), DateCalendarValue, 112) as int) as 'DateKey',
cast(DateCalendarValue as date) as 'FullDate',
datepart(weekday, DateCalendarValue) as 'DayNumberOfWeek',
datename(weekday, DateCalendarValue) as 'DayNameOfWeek',
case datename(dw, DateCalendarValue)
when 'Saturday' then 'Weekend'
when 'Sunday' then 'Weekend'
else 'Weekday'
end as 'WeekDayType',
datepart(day, DateCalendarValue) as'DayNumberOfMonth',
datepart(dayofyear, DateCalendarValue) as 'DayNumberOfYear',
datepart(week, DateCalendarValue) as 'WeekNumberOfYear',
datename(month, DateCalendarValue) as 'MonthNameOfYear',
datepart(month, DateCalendarValue) as 'MonthNumberOfYear',
datepart(quarter, DateCalendarValue) as 'QuarterNumberCalendar',
'Q' + cast(datepart(quarter, DateCalendarValue) as nvarchar) as 'QuarterNameCalendar',
case
when datepart(month, DateCalendarValue) <= 6 then 1
when datepart(month, DateCalendarValue) > 6 then 2
end as 'SemesterNumberCalendar',
case
when datepart(month, DateCalendarValue) < = 6 then 'First Semester'
when datepart(month, DateCalendarValue) > 6 then 'Second Semester'
end as 'SemesterNameCalendar',
datepart(year, DateCalendarValue) as 'YearCalendar',
datepart(month, FiscalCounter) as 'MonthNumberFiscal',
datepart(quarter, FiscalCounter) as 'QuarterNumberFiscal',
'Q' + cast(datepart(quarter, FiscalCounter) as nvarchar) as 'QuarterNameFiscal',
case
when datepart(month, FiscalCounter) < = 6 then 1
when datepart(month, FiscalCounter) > 6 then 2
end as 'SemesterNumberFiscal',
case
when datepart(month, FiscalCounter) < = 6 then 'First Semester'
when datepart(month, FiscalCounter) > 6 then 'Second Semester'
end as 'SemesterNameFiscal',
datepart(year, FiscalCounter) as 'YearFiscal'
from DateDimension
order by
DateCalendarValue
option (maxrecursion 0);
-- DimProduct
insert into production_FinanceDW.dbo.DimProduct
(
ProductID,
ProductName,
PromotionYear
)
select
p.ProductID,
ProductName,
PromotionYear
from FinanceDB.dbo.Product p
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Promotion pm on p.ProductID = pm.ProductID;
-- DimSalesLocation
insert into production_FinanceDW.dbo.DimSalesLocation
(
RegionID,
CountryID,
SegmentID,
CountryName,
SegmentName
)
select
RegionID,
c.CountryID,
s.SegmentID,
CountryName,
SegmentName
from FinanceDB.dbo.Region r
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID;
-- DimSalesPerson
insert into production_FinanceDW.dbo.DimSalesPerson
(
SalesPersonID,
FirstName,
LastName,
Gender,
HireDate,
DayOfBirth,
DaysOfLeave,
DaysOfSickLeave
)
select
SalesPersonID,
FirstName,
LastName,
Gender,
HireDate,
DayOfBirth,
DaysOfLeave,
DaysOfSickLeave
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesPerson;
-- Fact_SalePerformance
with fsp_1(SalesYear, SalesPersonID, RegionID, CountryName, SegmentName, TotalYearlyKPI, TotalMonthlyKPI) as
(
select
SalesYear,
sp.SalesPersonID,
r.RegionID,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
sum(KPI) as TotalYearlyKPI,
sum(KPI) / 12 as TotalMonthlyKPI
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesPerson sp
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesKPI sk on sp.SalesPersonID = sk.SalesPersonID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on sp.SalesPersonID = sr.SalesPersonID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Region r on sr.RegionID = r.RegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
group by
SalesYear,
sp.SalesPersonID,
r.RegionID,
CountryName,
SegmentName
),
fsp_2(SalesYear, CountryName, SegmentName, TotalSalesPrice) as
(
select
year(SalesOrderDate) as SalesYear,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
sum(SalePrice) as TotalSalesPrice
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Region r on sr.RegionID = r.RegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so on sr.SalesRegionID = so.SalesRegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li on so.SalesOrderID = li.SalesOrderID
group by
year(SalesOrderDate),
CountryName,
SegmentName
),
fsp_3 (
SalesDate,
SalesYear,
SalesMonth,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
TotalMonthlyPrice
) as
(
select distinct
concat(year(SalesOrderDate), RIGHT('0' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(2), Month( SalesOrderDate )), 2), '01') as SalesDate,
year(SalesOrderDate) as SalesYear,
month(SalesOrderDate) as SalesMonth,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
sum(SalePrice) as TotalMonthlyPrice
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li on so.SalesOrderID = li.SalesOrderID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on so.SalesRegionID = sr.SalesRegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Region r on sr.RegionID = r.RegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
group by
concat(year(SalesOrderDate), RIGHT('0' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(2), Month( SalesOrderDate )), 2), '01'),
year(SalesOrderDate),
month(SalesOrderDate),
CountryName,
SegmentName
)
insert into production_FinanceDW.dbo.FactSalePerformance
select
SalesDate,
fsp_1.SalesPersonID,
fsp_1.RegionID,
TotalYearlyKPI,
TotalSalesPrice,
round(sum((TotalSalesPrice / TotalYearlyKPI) * 100), 2) as AnnualPerformance,
TotalMonthlyKPI,
TotalMonthlyPrice,
round(sum((TotalMonthlyPrice / TotalMonthlyKPI) * 100), 2) as AnnualPerformance
from fsp_1
inner join fsp_2 on fsp_1.SalesYear = fsp_2.SalesYear
and fsp_1.CountryName = fsp_2.CountryName
and fsp_1.SegmentName = fsp_2.SegmentName
inner join fsp_3 on fsp_1.SalesYear = fsp_3.SalesYear
and fsp_1.CountryName = fsp_3.CountryName
and fsp_1.SegmentName = fsp_3.SegmentName
group by
SalesDate,
fsp_1.SalesPersonID,
fsp_1.RegionID,
TotalYearlyKPI,
TotalSalesPrice,
TotalMonthlyKPI,
TotalMonthlyPrice
order by
fsp_3.SalesDate;
-- Fact_SaleOrder
with fso_1(
SaleYear,
RegionID,
SalesPersonID,
ProductID,
SalesOrderID,
UnitsSold,
SalePrice
) as
(
select distinct
convert(int, convert(varchar(8), SalesOrderDate, 112)) as SaleYear,
sr.RegionID,
so.SalesPersonID,
li.ProductID,
so.SalesOrderID,
li.UnitsSold,
li.SalePrice
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so on li.SalesOrderID = so.SalesOrderID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on so.SalesRegionID = sr.SalesRegionID
),
fso_2(
SaleYear,
RegionID,
SalesPersonID,
ProductID,
SalesOrderID,
TotalSalesPrice,
TotalCost,
TotalRRP,
TotalItems,
GrossProfit,
PromotionRate,
Margin,
PercentageDiscount
) as
(
select
convert(int, convert(varchar(8), SalesOrderDate, 112)) as SaleYear,
sr.RegionID,
sr.SalesPersonID,
pc.ProductID,
so.SalesOrderID,
sum(li.SalePrice * li.UnitsSold) as TotalSalesPrice,
sum(pc.ManufacturingPrice * li.UnitsSold) as TotalCost,
sum(pc.RRP * li.UnitsSold) as TotalRRP,
sum(li.UnitsSold) as TotalItems,
sum((li.SalePrice - pc.ManufacturingPrice) * li.UnitsSold) as GrossProfit,
sum(case when li.PromotionID = 0 then 0.0 else 1.0 end) / count(*) as PromotionRate,
round(case
when sum(SalePrice) = 0 then 0
else sum(SalePrice - (pc.ManufacturingPrice * li.UnitsSold)) / sum(SalePrice)
end, 2) as Margin,
round(sum((pc.RRP * li.UnitsSold) - SalePrice) / sum(pc.RRP * li.UnitsSold), 2) as PercentageDiscount
from FinanceDB.dbo.ProductCost pc
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li on pc.ProductID = li.ProductID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so on li.SalesOrderID = so.SalesOrderID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on so.SalesRegionID = sr.SalesRegionID
group by
convert(int, convert(varchar(8), SalesOrderDate, 112)),
sr.RegionID,
sr.SalesPersonID,
pc.ProductID,
so.SalesOrderID
)
insert into production_FinanceDW.dbo.FactSaleOrder
select
fso_1.SaleYear,
fso_1.SalesOrderID,
fso_1.RegionID,
fso_1.SalesPersonID,
fso_1.ProductID,
fso_1.UnitsSold,
fso_1.SalePrice,
fso_2.TotalSalesPrice,
fso_2.TotalCost,
fso_2.GrossProfit,
fso_2.TotalRRP,
fso_2.TotalItems,
fso_2.PromotionRate,
fso_2.Margin,
fso_2.PercentageDiscount
from fso_1
inner join fso_2 on fso_1.SaleYear = fso_2.SaleYear
and fso_1.RegionID = fso_2.RegionID
and fso_1.SalesPersonID = fso_2.SalesPersonID
and fso_1.ProductID = fso_2.ProductID
and fso_1.SalesOrderID = fso_2.SalesOrderID
order by
fso_1.SaleYear,
fso_1.RegionID,
fso_1.SalesPersonID,
fso_1.ProductID,
fso_1.SalesOrderID;
end;
go
-- >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-- Execute Insert Into procedure
exec insert_into;
go
Appendix B
-- >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-- Views for fact tables
-- Fact_SalePerformance
drop view fact_sp;
go
create view fact_sp as
with fsp_1(SalesYear, SalesPersonID, RegionID, CountryName, SegmentName, TotalYearlyKPI, TotalMonthlyKPI) as
(
select
SalesYear,
sp.SalesPersonID,
r.RegionID,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
sum(KPI) as TotalYearlyKPI,
sum(KPI) / 12 as TotalMonthlyKPI
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesPerson sp
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesKPI sk on sp.SalesPersonID = sk.SalesPersonID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on sp.SalesPersonID = sr.SalesPersonID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Region r on sr.RegionID = r.RegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
group by
SalesYear,
sp.SalesPersonID,
r.RegionID,
CountryName,
SegmentName
),
fsp_2(SalesYear, CountryName, SegmentName, TotalSalesPrice) as
(
select
year(SalesOrderDate) as SalesYear,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
sum(SalePrice) as TotalSalesPrice
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Region r on sr.RegionID = r.RegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so on sr.SalesRegionID = so.SalesRegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li on so.SalesOrderID = li.SalesOrderID
group by
year(SalesOrderDate),
CountryName,
SegmentName
),
fsp_3 (
SalesDate,
SalesYear,
SalesMonth,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
TotalMonthlyPrice
) as
(
select distinct
concat(year(SalesOrderDate), RIGHT('0' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(2), Month( SalesOrderDate )), 2), '01') as SalesDate,
year(SalesOrderDate) as SalesYear,
month(SalesOrderDate) as SalesMonth,
CountryName,
SegmentName,
sum(SalePrice) as TotalMonthlyPrice
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li on so.SalesOrderID = li.SalesOrderID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on so.SalesRegionID = sr.SalesRegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Region r on sr.RegionID = r.RegionID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
group by
concat(year(SalesOrderDate), RIGHT('0' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(2), Month( SalesOrderDate )), 2), '01'),
year(SalesOrderDate),
month(SalesOrderDate),
CountryName,
SegmentName
)
select
SalesDate,
fsp_1.SalesPersonID,
fsp_1.RegionID,
TotalYearlyKPI,
TotalSalesPrice,
round(sum((TotalSalesPrice / TotalYearlyKPI) * 100), 2) as AnnualPerformance,
TotalMonthlyKPI,
TotalMonthlyPrice,
round(sum((TotalMonthlyPrice / TotalMonthlyKPI) * 100), 2) as MonthlylPerformance
from fsp_1
inner join fsp_2 on fsp_1.SalesYear = fsp_2.SalesYear
and fsp_1.CountryName = fsp_2.CountryName
and fsp_1.SegmentName = fsp_2.SegmentName
inner join fsp_3 on fsp_1.SalesYear = fsp_3.SalesYear
and fsp_1.CountryName = fsp_3.CountryName
and fsp_1.SegmentName = fsp_3.SegmentName
group by
SalesDate,
fsp_1.SalesPersonID,
fsp_1.RegionID,
TotalYearlyKPI,
TotalSalesPrice,
TotalMonthlyKPI,
TotalMonthlyPrice;
go
-- Fact_SaleOrder
drop view fact_so;
go
create view fact_so as
with fso_1(
SaleYear,
RegionID,
SalesPersonID,
ProductID,
SalesOrderID,
UnitsSold,
SalePrice
) as
(
select distinct
convert(int, convert(varchar(8), SalesOrderDate, 112)) as SaleYear,
sr.RegionID,
so.SalesPersonID,
li.ProductID,
so.SalesOrderID,
li.UnitsSold,
li.SalePrice
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so on li.SalesOrderID = so.SalesOrderID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on so.SalesRegionID = sr.SalesRegionID
),
fso_2(
SaleYear,
RegionID,
SalesPersonID,
ProductID,
SalesOrderID,
TotalSalesPrice,
TotalCost,
TotalRRP,
TotalItems,
GrossProfit,
PromotionRate,
Margin,
PercentageDiscount
) as
(
select
convert(int, convert(varchar(8), SalesOrderDate, 112)) as SaleYear,
sr.RegionID,
sr.SalesPersonID,
pc.ProductID,
so.SalesOrderID,
sum(li.SalePrice * li.UnitsSold) as TotalSalesPrice,
sum(pc.ManufacturingPrice * li.UnitsSold) as TotalCost,
sum(pc.RRP * li.UnitsSold) as TotalRRP,
sum(li.UnitsSold) as TotalItems,
sum((li.SalePrice - pc.ManufacturingPrice) * li.UnitsSold) as GrossProfit,
sum(case when li.PromotionID = 0 then 0.0 else 1.0 end) / count(*) as PromotionRate,
round(case
when sum(SalePrice) = 0 then 0
else sum(SalePrice - (pc.ManufacturingPrice * li.UnitsSold)) / sum(SalePrice)
end, 2) as Margin,
round(sum((pc.RRP * li.UnitsSold) - SalePrice) / sum(pc.RRP * li.UnitsSold), 2) as PercentageDiscount
from FinanceDB.dbo.ProductCost pc
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrderLineItem li on pc.ProductID = li.ProductID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesOrder so on li.SalesOrderID = so.SalesOrderID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.SalesRegion sr on so.SalesRegionID = sr.SalesRegionID
group by
convert(int, convert(varchar(8), SalesOrderDate, 112)),
sr.RegionID,
sr.SalesPersonID,
pc.ProductID,
so.SalesOrderID
)
select
fso_1.SaleYear,
fso_1.SalesOrderID,
fso_1.RegionID,
fso_1.SalesPersonID,
fso_1.ProductID,
fso_1.UnitsSold,
fso_1.SalePrice,
fso_2.TotalSalesPrice,
fso_2.TotalCost,
fso_2.GrossProfit,
fso_2.TotalRRP,
fso_2.TotalItems,
fso_2.PromotionRate,
fso_2.Margin,
fso_2.PercentageDiscount
from fso_1
inner join fso_2 on fso_1.SaleYear = fso_2.SaleYear
and fso_1.RegionID = fso_2.RegionID
and fso_1.SalesPersonID = fso_2.SalesPersonID
and fso_1.ProductID = fso_2.ProductID
and fso_1.SalesOrderID = fso_2.SalesOrderID;
go
-- >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-- Merge tables
drop procedure if exists table_merge;
go
create procedure table_merge
as
begin
-- DimProduct
with dp_cte (ProductID, ProductName, PromotionYear) as
(
select
p.ProductID,
p.ProductName,
pm.PromotionYear
from FinanceDB.dbo.Product p
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Promotion pm on p.ProductID = pm.ProductID
)
merge into production_FinanceDW.dbo.DimProduct as Target
using dp_cte as Source
on Target.ProductID = Source.ProductID
and Target.ProductName = Source.ProductName
and Target.PromotionYear = Source.PromotionYear
when matched then
update set
Target.ProductName = Source.ProductName,
Target.PromotionYear = Source.PromotionYear
when not matched then
insert (
ProductName,
PromotionYear
)
values (
Source.ProductName,
Source.PromotionYear
);
-- DimSalesLocation
with dsl_cte (
RegionID,
CountryID,
SegmentID,
CountryName,
SegmentName
) as
(
select
RegionID,
c.CountryID,
s.SegmentID,
CountryName,
SegmentName
from FinanceDB.dbo.Region r
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Country c on r.CountryID = c.CountryID
inner join FinanceDB.dbo.Segment s on r.SegmentID = s.SegmentID
)
merge into production_FinanceDW.dbo.DimSalesLocation as Target
using dsl_cte as Source
on Target.RegionID = Source.RegionID
and Target.CountryID = Source.CountryID
and Target.SegmentID = Source.SegmentID
when matched then
update set
Target.CountryID = Source.CountryID,
Target.SegmentID = Source.SegmentID,
Target.CountryName = Source.CountryName,
Target.SegmentName = Source.SegmentName
when not matched then
insert (
CountryID,
SegmentID,
CountryName,
SegmentName
)
values (
Source.CountryID,
Source.SegmentID,
Source.CountryName,
Source.SegmentName
);
-- DimSalesPerson
with dsp_cte (
SalesPersonID,
FirstName,
LastName,
Gender,
HireDate,
DayOfBirth,
DaysOfLeave,
DaysOfSickLeave
) as
(
select
SalesPersonID,
FirstName,
LastName,
Gender,
HireDate,
DayOfBirth,
DaysOfLeave,
DaysOfSickLeave
from FinanceDB.dbo.SalesPerson
)
merge into production_FinanceDW.dbo.DimSalesPerson as Target
using dsp_cte as Source
on Target.SalesPersonID = Source.SalesPersonID
when matched then
update set
Target.FirstName = Source.FirstName,
Target.LastName = Source.LastName,
Target.Gender = Source.Gender,
Target.HireDate = Source.HireDate,
Target.DayOfBirth = Source.DayOfBirth,
Target.DaysOfLeave = Source.DaysOfLeave,
Target.DaysOfSickLeave = Source.DaysOfSickLeave
when not matched then
insert (
FirstName,
LastName,
Gender,
HireDate,
DayOfBirth,
DaysOfLeave,
DaysOfSickLeave
)
values (
Source.FirstName,
Source.LastName,
Source.Gender,
Source.HireDate,
Source.DayOfBirth,
Source.DaysOfLeave,
Source.DaysOfSickLeave
);
-- Fact_SalePerformance
merge into production_FinanceDW.dbo.FactSalePerformance as Target
using fact_sp as Source
on Target.DateKey = Source.SalesDate
and Target.SalesPersonID = Source.SalesPersonID
and Target.RegionID = Source.RegionID
when matched then
update set
Target.TotalAnnualKPI = Source.TotalYearlyKPI,
Target.AnnualSalesPrice = Source.TotalSalesPrice,
Target.AnnualPerformance = Source.AnnualPerformance,
Target.TotalMonthlylKPI = Source.TotalMonthlyKPI,
Target.MonthlySalesPrice = Source.TotalMonthlyPrice,
Target.MonthlyPerformance = Source.MonthlylPerformance
when not matched then
insert (
TotalAnnualKPI,
AnnualSalesPrice,
AnnualPerformance,
TotalMonthlylKPI,
MonthlySalesPrice,
MonthlyPerformance
)
values (
Source.TotalYearlyKPI,
Source.TotalSalesPrice,
Source.AnnualPerformance,
Source.TotalMonthlyKPI,
Source.TotalMonthlyPrice,
Source.MonthlylPerformance
);
-- Fact_SaleOrder
merge into production_FinanceDW.dbo.FactSaleOrder as Target
using fact_so as Source
on Target.DateKey = Source.SaleYear
and Target.RegionID = Source.RegionID
and Target.SalesPersonID = Source.SalesPersonID
and Target.ProductID = Source.ProductID
and Target.SalesOrderID = Source.SalesOrderID
and Target.UnitsSold = Source.UnitsSold
and Target.SalePrice = Source.SalePrice
when matched then
update set
Target.TotalSalesPrice = Source.TotalSalesPrice,
Target.TotalCost = Source.TotalCost,
Target.TotalRRP = Source.TotalRRP,
Target.TotalItems = Source.TotalItems,
Target.GrossProfit = Source.GrossProfit,
Target.PromotionRate = Source.PromotionRate,
Target.Margin = Source.Margin,
Target.PercentageDiscount = Source.PercentageDiscount
when not matched then
insert (
TotalSalesPrice,
TotalCost,
GrossProfit,
TotalRRP,
TotalItems,
PromotionRate,
Margin,
PercentageDiscount
)
values (
Source.TotalSalesPrice,
Source.TotalCost,
Source.GrossProfit,
Source.TotalRRP,
Source.TotalItems,
Source.PromotionRate,
Source.Margin,
Source.PercentageDiscount
);
end;
go
-- >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-- Execute Merge Into procedure
exec table_merge;
go
